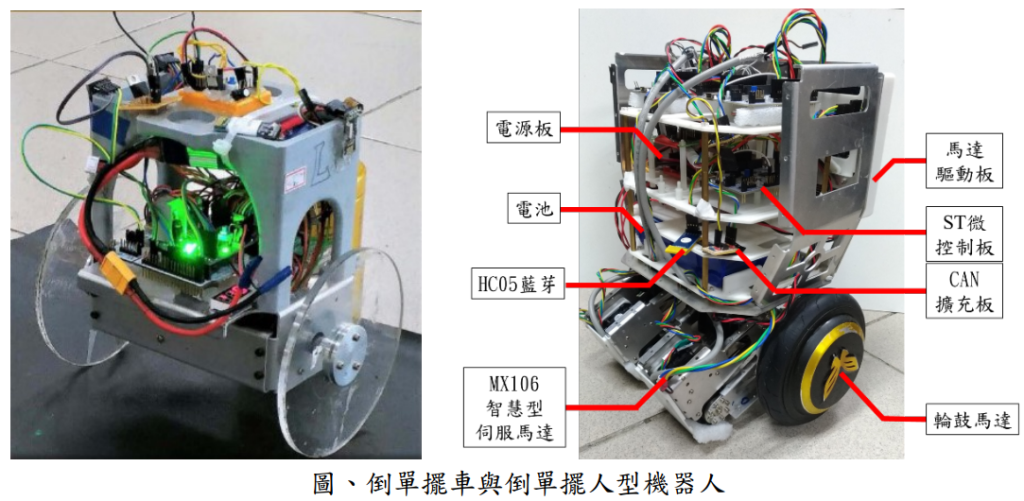
This research aims to develop systematic methodologies to perform sensor fusion, balancing control, and whole-body posture control on a humanoid wheel inverted pendulum (WIP) robots. For sensor fusion, a novel pitch angle estimator is proposed by merging the measurements for two IMU’s. Such an estimator is meant to eliminate the error caused by motion acceleration when estimating the pitch angle for feedback purposes. For the balancing control, a controller that provides robust stability to the variations of the CoM height is proposed. Its feedback gain matrix is computed by solving a set of linear matrix inequalities so that Lyapunov stability can be achieved on a linear parameter varying (LPV) model. For the whole-body posture control, it contains two controllers: the centroid controller and the roll angle controller. The objective of the centroid controller is to make the centroid follow a reference command while keeping the robot body in an upright osition. The centroid controller is PI-based and is designed by constructing a three-link model and inverting the differential kinematic relationship between the joint velocities and the centroid velocities. On the other hand, the roll angle controller is to regulate the robot’s roll angle. It is also PI-based and is designed using a five-link model that describes the kinematic relations between the roll angle and the joint angles of the legs. The sensor fusion and control methods are implemented on a humanoid WIP robot built in-house. Simulations and experiments are conducted to validate the feasibility of the proposed approaches.