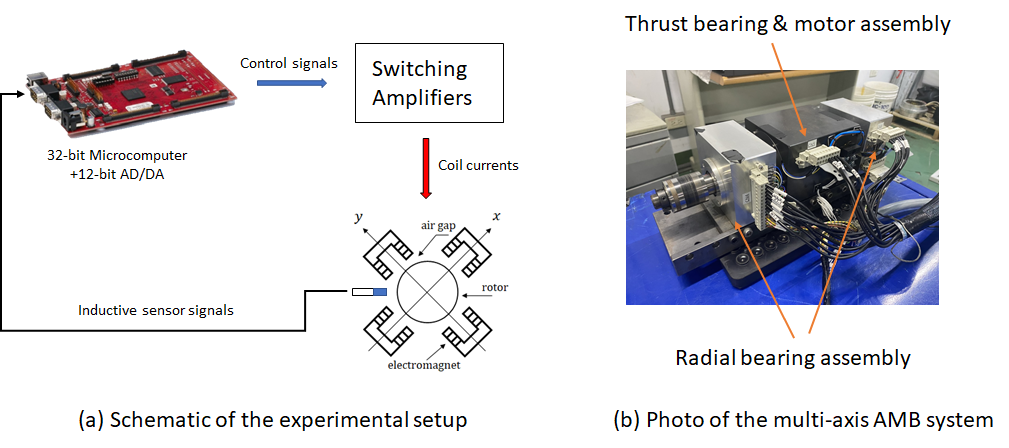
Closed-Loop System Identification of High-Speed Magnetic Levitation Spindle
In response to the open-loop instability of magnetic bearing systems, this research develops a closed-loop identification method to obtain an accurate plant model for controller design. The identification method is based on a decentralized and decoupling control architecture, which allows the decoupling of the multi-input-multi-output (MIMO) system into two single-input-single-output (SISO) systems for simplifying the …
Closed-Loop System Identification of High-Speed Magnetic Levitation Spindle Read More »